Sebaceous hyperplasia is a common skin condition characterized by small, benign bumps that typically appear on the face. These bumps occur when sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oil...
READ MORE
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a common skin condition characterized by small, benign bumps that typically appear on the face. These bumps occur when sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oil (sebum) to lubricate the skin, become enlarged. The condition is most commonly seen in middle-aged and older adults and can be influenced by hormonal changes, genetics, and certain medications. Although sebaceous hyperplasia is harmless, it can sometimes be mistaken for other skin conditions such as basal cell carcinoma. Treatment options, if desired for cosmetic reasons, include topical medications, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and electrosurgery.
During treatment for sebaceous hyperplasia, the specific method used will determine the procedure. For example:
Topical Medications: If using topical treatments, a dermatologist will apply or prescribe creams containing ingredients such as retinoids or acids that help reduce the size of sebaceous glands.
Laser Therapy: In laser treatment, a specialized laser targets the sebaceous glands, breaking down the excess tissue. Protective eyewear is used to safeguard your eyes from the laser. The procedure is generally brief and involves only slight discomfort.
Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves applying liquid nitrogen to freeze the bumps. The sensation is often described as a brief, intense cold followed by tingling.
Electrosurgery: This method uses an electric current to burn off the excess tissue. To reduce discomfort during the procedure, a local anesthetic may be used.
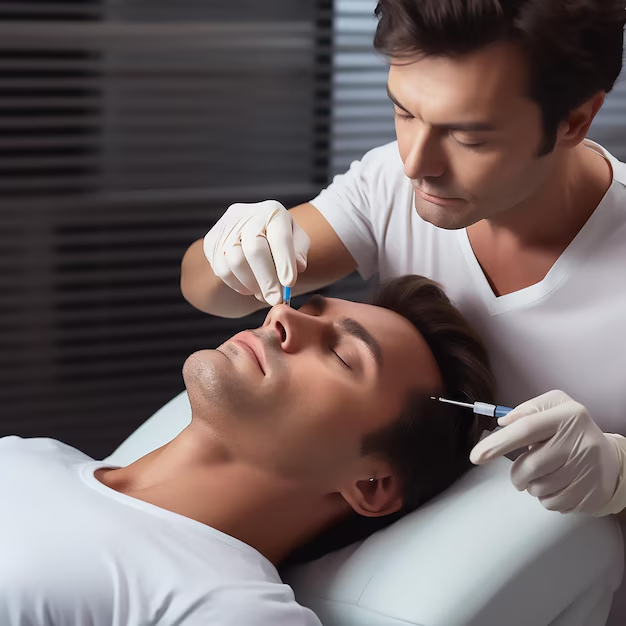
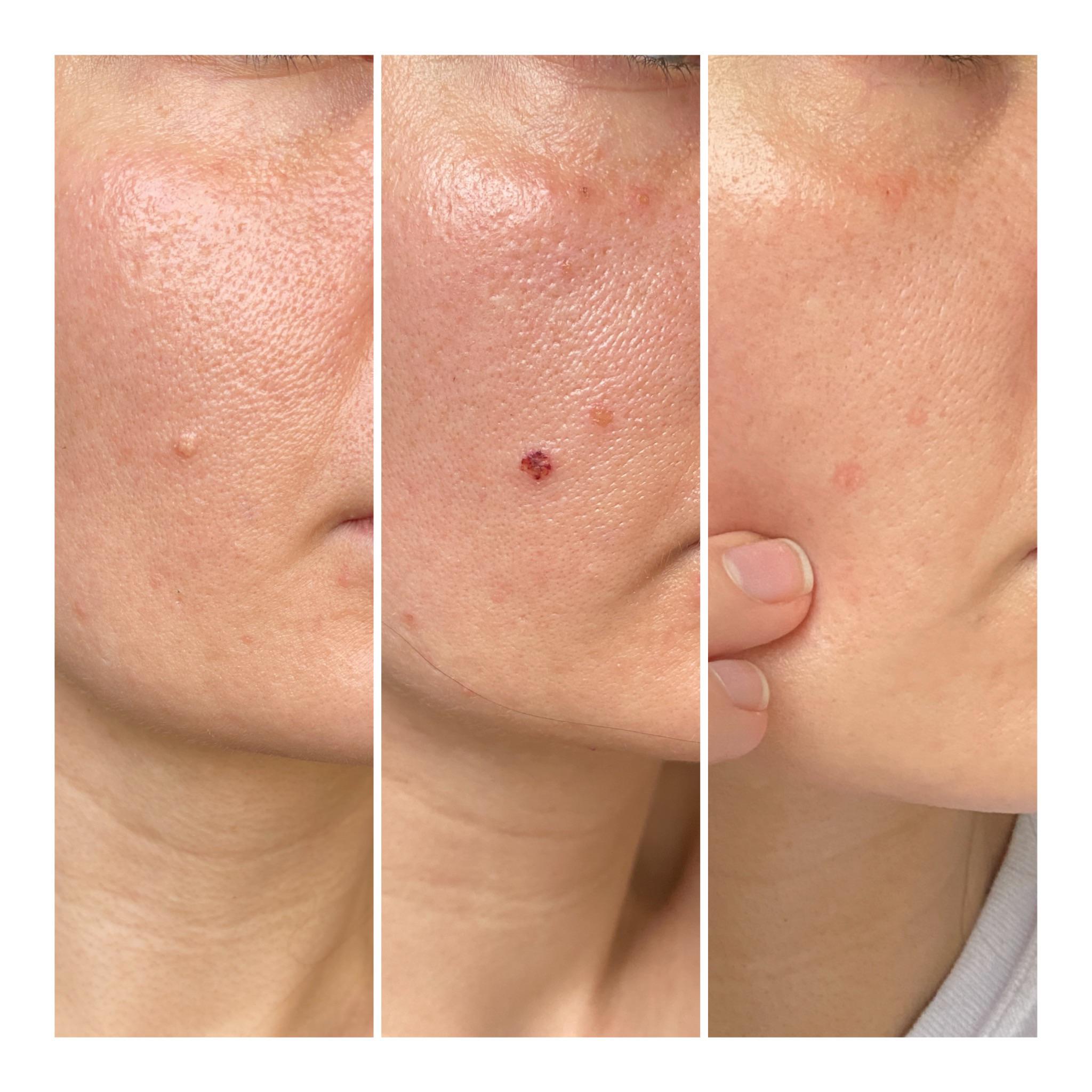
After treatment for sebaceous hyperplasia, patients might experience some redness, swelling, or mild discomfort in the treated area. These effects are usually temporary and reduce within a few days. It is important to keep the treated area clean and protected from excessive sun exposure.
Topical Medications: Continued use as prescribed will help maintain results and prevent new lesions from forming.
Laser Therapy: Redness and swelling might persist for a few days. Gentle skincare and avoiding harsh products are recommended.
Cryotherapy: The treated area may blister or scab over. It's crucial not to pick at the scabs to avoid scarring.
Electrosurgery: Similar to other methods, redness and swelling are common and typically subside within a week. Keeping the area clean and avoiding direct sun exposure is advised.
Follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed, ensuring optimal results and addressing any new lesions that may appear.
Copyright © Sparsh. All Rights Reserved by Multiple Revolution